Imagine a digital notebook that is shared among many people. Every time someone makes a change or adds new information, it’s like writing a new entry in the notebook. But instead of just one notebook, there are many copies, and everyone has one. When a new entry is added, it’s added to all the notebooks at the same time. This way, everyone has the same information, and no one can cheat or change the records without everyone else knowing.
This “digital notebook” is called a blockchain. It’s a way to record information in a way that is:
- Shared: Everyone in the network has a copy of the blockchain.
- Transparent: All transactions are publicly viewable.
- Secure: Once a transaction is recorded, it cannot be altered or deleted.
- Decentralized: No single person or entity controls the blockchain.
How does it work?
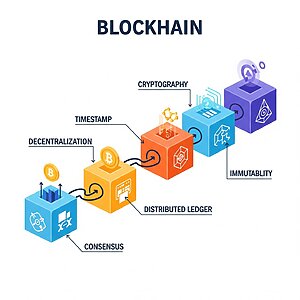
Blockchain stores data in “blocks” that are linked together in a “chain.” Each block contains:
- Data: This could be information about transactions, like who sent money to whom, or any other kind of data.
- Hash: A unique code, like a fingerprint, that identifies the block.
- Hash of the previous block: This links the current block to the previous one, forming a chain.
When a new transaction happens, it’s grouped with other recent transactions into a new block. This new block is then added to the chain. Because each block contains the hash of the previous block, it’s nearly impossible to change any information in an old block without changing all subsequent blocks. This makes the blockchain very secure.
Examples of Blockchain Use
- Cryptocurrencies: Bitcoin and other cryptocurrencies use blockchain to record all transactions. This is why it’s very difficult to counterfeit or double-spend cryptocurrencies.
- Supply Chain Management: Companies can use blockchain to track products as they move from suppliers to consumers. This helps ensure the authenticity and quality of goods. For example, a food company could use blockchain to track the origin and journey of their products, providing consumers with detailed information about where their food comes from.
- Voting Systems: Blockchain can be used to create secure and transparent voting systems, reducing the risk of fraud.
- Digital Identity: Blockchain can help individuals control their digital identities and share their data securely.
- Smart Contracts: These are self-executing contracts stored on the blockchain. They automatically execute when certain conditions are met. For example, a smart contract could automatically release payment to a seller once a buyer confirms receipt of goods.
Benefits of Blockchain
- Increased Transparency: All transactions are recorded on a public ledger, making it easier to track and verify information.
- Enhanced Security: The decentralized and cryptographic nature of blockchain makes it very difficult to hack or manipulate.
- Greater Efficiency: Blockchain can streamline processes and reduce the need for intermediaries, leading to faster and cheaper transactions.
- Improved Traceability: Blockchain makes it easier to track the origin and movement of goods and information.
Ultimately, Blockchain is more than just the technology behind cryptocurrencies; it’s a foundational innovation for secure and transparent record-keeping. By enabling shared, unchangeable ledgers, it offers transformative potential across various industries, promising enhanced trust, efficiency, and accountability in our increasingly digital world. Its decentralized nature fundamentally reshapes how we can manage and verify information, paving the way for a new era of digital interactions.
It’s important to note that cryptocurrency remains an unregulated digital asset, not recognized as legal tender, and is subject to market risks. The information provided should not be considered financial or trading advice. CryptoNow holds no responsibility for any investment decisions made based on the content of this article.